
Crowns, bridges, veneers
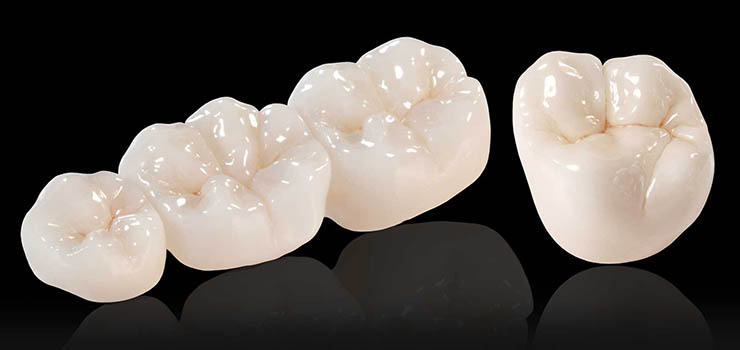
Modern dentistry devotes great attention to both function and aesthetics. Tooth loss may occur due to periodontal disease, unfavorable fracture line of the tooth, chronic lesions that cannot be treated, traumatic tooth avulsion, etc. Losing just one tooth can cause significant changes such as bone resorption (bone loss), lowering the bottom of the maxillary sinus, displacement of adjacent teeth into the edentulous area, extrusion (“eruption”) of the teeth in opposite jaw, the gap between teeth (diastema), midline shift , sensitivity of adjacent and opposite teeth due to bone loss and gingival recession, decreased chewing function on the side of tooth loss, as well as changes in temporomandibular joint. Therefore it is necessary to immediately consult a dentist about the possibilities for the replacement of missing teeth. Over time these changes can leave us with a poor choice of therapeutic methods.
Today, prosthodontics provides a wide range of esthetic solutions. The most common fixed restorations are ceramic (metal free) crowns and bridges, metal ceramic crowns and bridges, ceramic veneers, etc. In patients with several remaining teeth, the most frequent mobile restorations are partial metal dentures attached to metal ceramic crowns using specific elements (attachments), that provide better retention and stabilization and are maximally reduced and therefore more comfortable for patients to wear. In edentulous patients full dentures, implant supported dentures and implant supported bridges can be made.
Crowns or bridges?
In order to make a crown, we need a sufficient length of the root and of the remaining crown if possible. Your dentist can assess the present status by the clinical evaluation and x-ray analysis. If the tooth is severely damaged and needs to be extracted, it can be replaced by either an implant or bridge. Sometimes it is possible to close the extraction gap using orthodontic fixed appliances.
During the healing phase and throughout the whole manufacturing of restoration in the dental lab, temporary crowns and bridges will be provided for normal function and esthetics.
What is the difference between ceramic (non metal) and metaloceramic restorations?
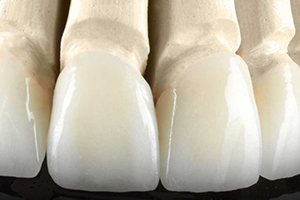
Unlike metaloceramic restorations, ceramic ones do not have a metal inner layer. In this way unnatural transparency of metal through the layers of ceramic can be avoided, making it more naturaly looking. Also, dark metal line along the edge of a crown cannot appear in ceramic restorations over a period of time.This is especially important for patients prone to gingival recessions and those with gummy smiles.
What are dental veneers?
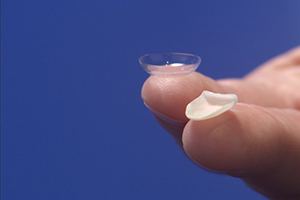
Veneer is a thin layer of ceramics, made to cover the visible sides of the tooth, and thereby mask the possible esthetic imperfections (discoloration, minor tooth fractions, small gaps between teeth). This method requires little or almost no grinding, and therefore is considered minimally invasive. Based on clinical examination, dentist will decide what type of veneers will be used in each case.
Can ceramic crowns always be replaced with ceramic veneers?
No. In cases of major dental tissue damage (extensive fillings, severe crown fracture, tooth wear-severe abrasion and attrition) it is necessary to make crowns (either ceramic or metal-ceramic), that often requires root canal treatment and placement of fiber posts.
Implants in prosthodontics

The increasingly frequent use of implants in everyday dental practice and extension of indications for their use by additional therapeutic methods opened up new possibilities of prosthetic care. Loss of just one or several teeth and unilateral or bilateral edentulism can be solved using fixed restorations on implants or a combination of implants and removable dentures.
Tooth extraction leads to atrophy (loss) of bone due to a lack of stimulation during the normal process of chewing. This greatly affects the esthetics of the face. The implants prevent bone loss by compensating for lost teeth in the region where the root once existed. This gives a huge advantage over bridges, that only replace a crown of the tooth.
The advantages of implant supported restorations are multiple:
- Avoiding unnecessary grinding of adjacent teeth and therefore preserving the dental tissue (in cases where one or several teeth are missing)
- Widening the indications for fixed restorations (in cases of shortened dental arches and large edentulous fields)
- Better stabilization and retention of full dentures , easier adjustment on a new restoration and reduced need for later corrections
- Maximally reduced full denture (significantly more comfortable for the patient)
Making of prosthetic restorations on implants – is it painful?
Unlike standard procedures, which require the use of local anesthesia, in implant supported restorations there is no need for that. After implant placement and a necessary healing period, making restoration is usually very comfortable for the patient. Our experience is that patients were pleasantly surprised by the whole procedure. In some cases, it is possible to make a temporary restoration immediately after the implant placement, but the definite decision is made by a surgeon and depending on current bone and gum status.
How long will the restoration last?
All restorations, weather made of ceramics or metal-ceramics, can last very long. However, you should always keep in mind that they are placed in the mouth, which is a very dynamic environment. Regular six months checkups, or even more often, are necessary to monitor the condition of teeth, gums and bone. Also, control x-rays are made from time to time. Possible related problems can be parodontopathy (paradentosis), caries on remaining tooth structure, chronic periapical lesions on root apex. Of course, the patient should dedicate time daily on maintaining oral hygiene and thus extend the life of prosthetic restoration, as well as their own teeth. Interdental brushes, specific floss and antiseptics must be regularly used.
Patients with removable dentures should also regularly visit the dentist. Bone resorption, wear of teeth in the denture, loosening the attachments (connecting elements) may require certain adjustments (relining the denture, replacing the attachment), and after a while, replacement with a new denture. On regular checkups , attention will be given on the remaining teeth (removal of concrements, replacement of old fillings, treatment of periodontal pockets).

